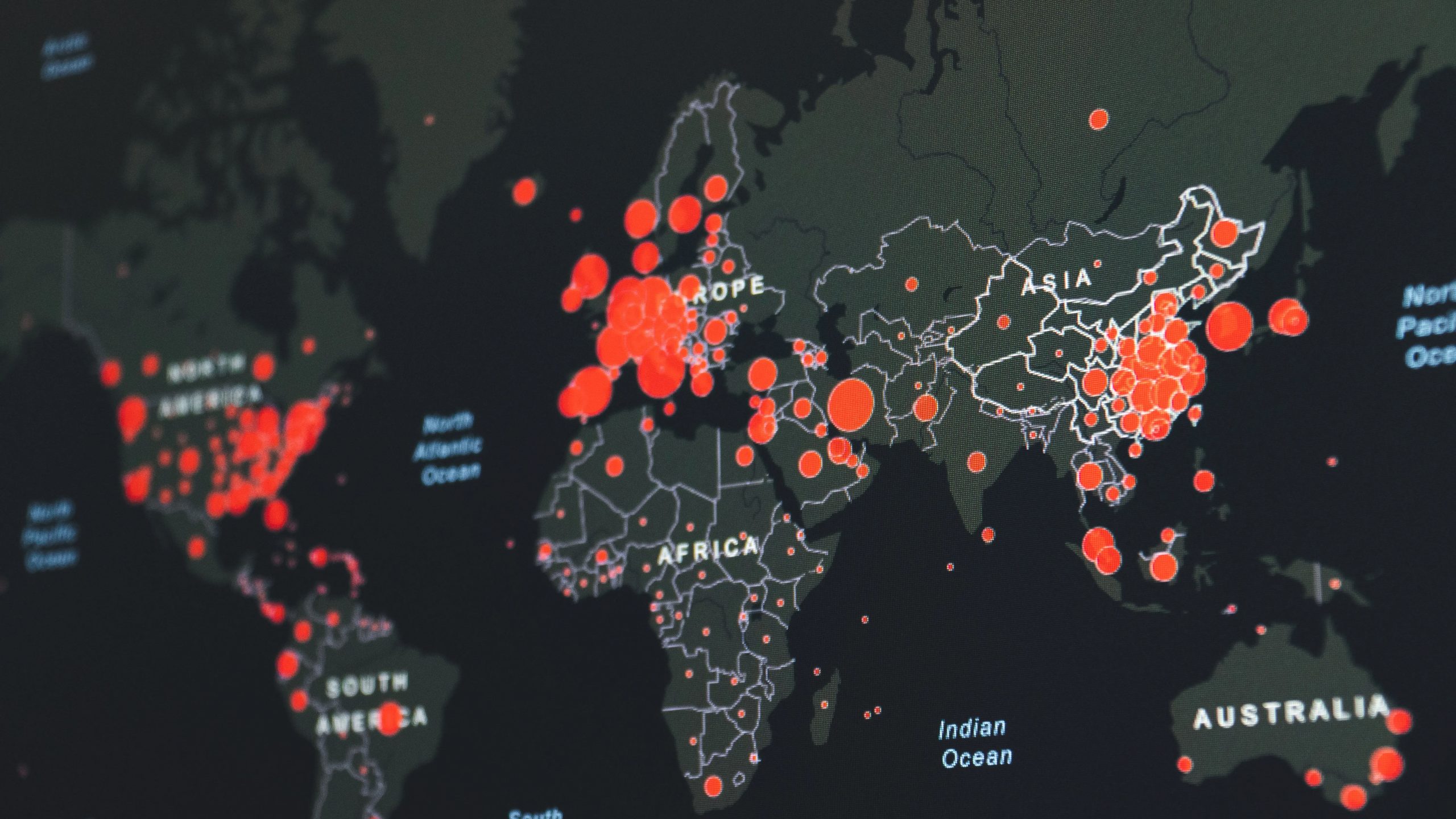
The Lambda strain of the coronavirus has spread nearly in 30 countries in the last four weeks and has left the World Health Organization perplexed. According to a leading Australian website, Lambda, known as the world’s most transmissible COVID-19 strain, has found its way into Australia and the UK.
Further research revealed that it “may be even more infectious than the Delta variant”, news.com.au reported.
Originally discovered in Peru, the mutation was dubbed as a ‘variant of concern‘ by the WHO and is related to 81% of the cases found in the country since April.
WHO had noted that it was “associated with substantive rates of community transmission in multiple countries.”
Peru currently has the highest COVID death rate anywhere in the world.
According to a report, in Peru, nearly 10% of those recorded as being infected end up dying. It has a death rate of nearly 600 for every 100,000 citizens, data showed.
“That would suggest its rate of transmission is higher than any other variant,” Cayetano Heredia University Professor Pablo Tsukayama was quoted as saying by news.com.au.
Tsukayama’s claims were seconded by Jeff Barrett from London’s COVID-19 Genomics Initiative.
“Lambda has a unique pattern of seven mutations in the spike protein that the virus uses to infect human cells. Researchers are particularly intrigued by one mutation called L452Q, which is similar to the L452R mutation to contribute to the high infectiousness of the Delta variant,” he told the Financial Times.
What makes Lambda, Delta highly contagious?
Since more and more cases are coming to the fore, a report from the scientists at the University of Chile suggests that the current vaccines are not effective against these strains.
“Our data show for the first time that mutations present in the spike protein of the Lambda variant confer escape to neutralising antibodies and increased infectivity,” the scientists said.
Their study also warned that should Lambda spread, it would result in a rapid spread.
“Considering that this variant has rapidly spread in Peru, Ecuador, Chile and Argentina, we believe that Lambda has a considerable potential to become a variant of concern,” their paper read.
WHO, on the other hand, has maintained that “further studies are required to validate the continued effectiveness of vaccines” against the new strain.
Dr Eric Feigl-Ding, an epidemiologist and health economist, in a Twitter thread said: “Delta is still a bigger thread than Lambda. A grenade in hand with the pin pulled (Delta) is more dangerous than an unknown possible-grenade-looking variant in the sky (Lambda).”